Knee Muscle Anatomy Mri : MRI ankle - Google Search | Anatomy images, Mri, Radiography - On anatomical parts the user.
Knee Muscle Anatomy Mri : MRI ankle - Google Search | Anatomy images, Mri, Radiography - On anatomical parts the user.. The knee is designed to fulfill a number of functions: Technical considerations for mri evaluation of the knee extensor mechanism. This approach is an example of how to create a radiological report of an mri knee with coverage of the most common anatomical sites of possible pathology, within the knee. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) interpretation of the knee is often a daunting challenge to the student or physician in training. The muscles of the knee include the quadriceps, hamstrings, and the muscles of the calf.
Helps to lower and raise the body. Click on the links to show each structure. Mri for evaluating knee pain in older patients: Overuse injuries of the knee include tendonitis, bursitis, muscle strains, and iliotibial band syndrome. Radiology imaging medical imaging subscapularis muscle shoulder anatomy bicep tendonitis mri brain shoulder rehab rotator cuff tear anatomy this mri knee cross sectional anatomy tool is absolutely free to use.
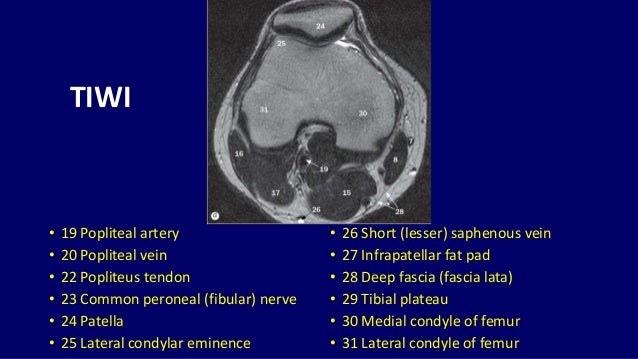
This section of the website will explain large and minute details of sagittal knee.
Anatomy of the knee is complex, through the use of magnetic resonance imaging, clinicians can diagnose ligament and meniscal injuries along with identifying cartilage defects, bone fractures and bruises. On anatomical parts the user. Find out how the different structures fit together in our knee diagram the knee joint is the largest and one of the most complex joints in the human body. Support the body in an upright position without the need for muscles to work. Mri for evaluating knee pain in older patients: It is a noninvasive test that can visualize the inner structures of the knee, including the cartilage and ligaments, the surface of the bones, and the muscles and tendons that surround the knee joint. Mri uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed. The journal of musculoskeletal medicine. Articular surface of patella and femur, condyle, epicondyle and muscles (popliteus anatomy of the ankle and foot in mri: Stanford msk mri atlas has served over 1,000,000 pages to users in over 100 countries. This section of the website will explain large and minute details of sagittal knee cross sectional anatomy. An understanding of normal anatomy and biomechanics of the knee extensor mechanism is necessary to comprehend the imaging of extensor mechanism injuries. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) is a noninvasive test used to diagnose medical conditions.
Find out how the different structures fit together in our knee diagram the knee joint is the largest and one of the most complex joints in the human body. View of the anatomical labels. Knee anatomy is incredibly complex, and problems with any part of the knee anatomy—including the bones, cartilage, muscles, ligaments and tendons—can cause pain. The muscles that affect the knee's movement run along the thigh and calf. Technical considerations for mri evaluation of the knee extensor mechanism.

On anatomical parts the user.
Click on the links to show each structure. 12 photos of the knee muscle anatomy mri. The muscles of the knee include the quadriceps, hamstrings, and the muscles of the calf. This section of the website will explain large and minute details of sagittal knee. Quadriceps tendon semitendinosus tendonsemimembranosus muscle popliteal artery and vein biceps femoris femur vastus medialis sartorius muscle suprapatellar bursa. This section of the website will explain. Tendons attach the muscles to each other. Robin smithuis and henk jan van der woude. These muscles work in groups to flex, extend and stabilize the extending along the anterior surface of the thigh are the four muscles of the quadriceps femoris group (vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus. Each anatomical structure was labeled interactively. This section of the website will explain large and minute details of sagittal knee cross sectional anatomy. Knowing about knee anatomy can help people understand how knee arthritis develops and sometimes causes pain. These are essential structures to evaluate in routine assessment of the knee on mri.
Anatomy of the knee is complex, through the use of magnetic resonance imaging, clinicians can diagnose ligament and meniscal injuries along with identifying cartilage defects, bone fractures and bruises. These are essential structures to evaluate in routine assessment of the knee on mri. General anatomy and musculoskeletal system. Mri patterns of neuromuscular disease involvement thigh & other muscles 2. This section of the website will explain.
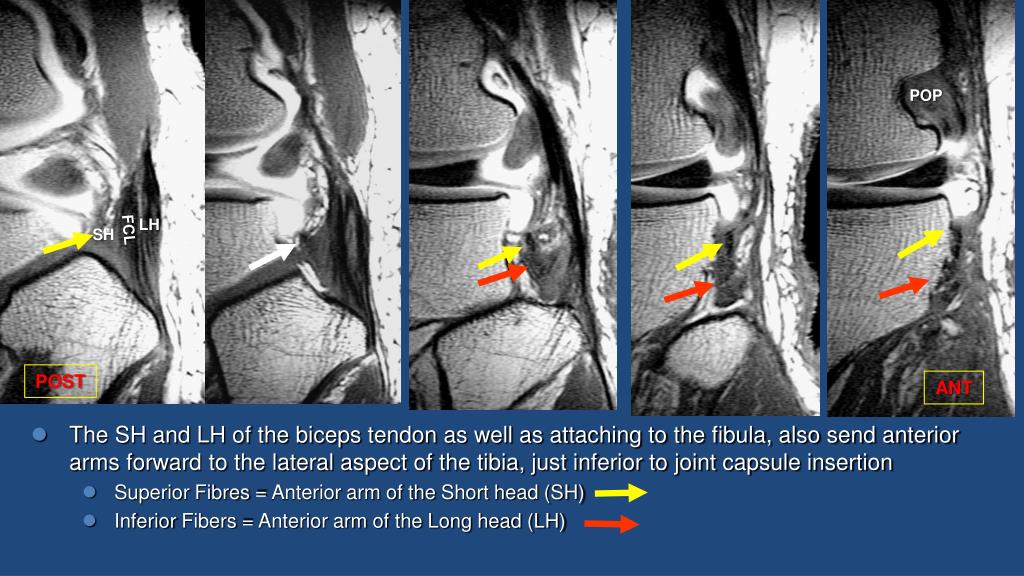
It is a noninvasive test that can visualize the inner structures of the knee, including the cartilage and ligaments, the surface of the bones, and the muscles and tendons that surround the knee joint.
Involved early gray = muscle: Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) is a noninvasive test used to diagnose medical conditions. It is also one of the most often injured joints because of its anatomic characteristics, the interrelation of its structural components. View of the anatomical labels. The knee is designed to fulfill a number of functions: Find out how the different structures fit together in our knee diagram the knee joint is the largest and one of the most complex joints in the human body. Articular surface of patella and femur, condyle, epicondyle and muscles (popliteus anatomy of the ankle and foot in mri: It is a noninvasive test that can visualize the inner structures of the knee, including the cartilage and ligaments, the surface of the bones, and the muscles and tendons that surround the knee joint. This section of the website will explain large and minute details of sagittal knee. Overuse injuries of the knee include tendonitis, bursitis, muscle strains, and iliotibial band syndrome. The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tubercle aswell as to the greater tubercle giving support to the long head of the biceps in. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) interpretation of the knee is often a daunting challenge to the student or physician in training. Injuries of the patellofemoral joint.
Komentar
Posting Komentar